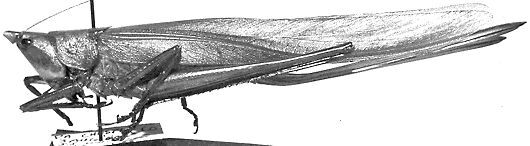
species
Neoconocephalus bivocatus Walker, Whitesell & Alexander, 1973
false robust conehead
Nomenclature (6)
- Neoconocephalus bivocatus Walker, Whitesell & Alexander, 1973: 326.
Holotype; male; ba2e7ca6-6710-4286-9b0f-3cc279adc0b8; deposited at: Florida State Museum (FSMC); United States: Maryland: 1.2 miles N of U.S. 40, Maryland Rt 7
- Neoconocephalus bivocatus Walker, Whitesell & Alexander, 1973 in Walker, 1975: 600.
- ... Show all ... (2)
- Neoconocephalus bivocatus Walker, Whitesell & Alexander, 1973 in Ney & Schul, 2017
- Neoconocephalus bivocatus Walker, Whitesell & Alexander, 1973 in Ney & Schul, 2019
Nomenclature references (6)
- Capinera, J.L., Scott, R.D. & Walker, T.J. (2004) In Field Guide to Grasshoppers, Katydids, and Crickets of the United States. Cornell University Press, Ithaca. 249 pp.
- Höbel, G. & Schul, J. (2007) Listening for males and bats: spectral processing in the hearing organ of Neoconocephalus bivocatus (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae). Journal of Comparative Physiology A Sensory Neural and Behavioral Physiology, 193(9), 917–925. Available at http://www.springerlink.com/content/6q6757g362w77862/
- ... Show all ... (2)
- Walker, T.J. (1975) Stridulatory movements in eight species of Neoconocephlus (Tettigoniidae). Journal of Insect Physiology, 21, 595–603. Available at http://entnemdept.ifas.ufl.edu/walker/Buzz/s160lw75.pdf
- Walker, T.J., Whitesell, J.J. & Alexander, R.D. (1973) The robust conehead: two widespread sibling species (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae: Neoconocephalus “robustus”). The Ohio Journal of Science, 73, 321–330. Available at http://entnemdept.ifas.ufl.edu/walker/Buzz/s160lw74.pdf
Descendants and synonyms
Stats
| Valid names | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Extant | Fossil | Invalid | Total | |
| species | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
